
First Steps in Agrello
A quick orientation for new Agrello users - understand your home screen and upload your first document in minutes.
Resources and Insights
Explore practical guides and explainers across Agrello topics. Browse focused libraries for e-signatures, contract management, document automation, and security.

A quick orientation for new Agrello users - understand your home screen and upload your first document in minutes.

Learn how Agrello's document container concept works and how documents move through lifecycle stages from draft to signed.

Discover what eIDAS is and why it matters for electronic signatures in the EU. Learn about the three signature levels, trust services, and how eIDAS ensures legal validity across Europe.

Discover how Large Language Models, advanced OCR, and machine learning converge to create AI-powered document automation that achieves 99%+ accuracy and human-level performance.

A clear explanation of electronic signatures (e-signatures), how they work, and the key benefits they bring to your business, including cost savings, efficiency, and enhanced security.

Think contract management is just for large enterprises? Think again. Learn what contract lifecycle management (CLM) really is and why it's one of the most important systems for a growing business.

Compare PDF (PAdES), ASIC (XAdES), and EDOC signature formats to choose the best option for your documents based on use case, signature requirements, and regional compliance needs.

Master Agrello's two-layer permission system: workspace roles (Owner, Administrator, Member) and folder permissions (Editor, Viewer). Control access, protect sensitive documents, and enable efficient team collaboration.

Calculate your document automation ROI with proven methodology. Discover how organizations achieve 248% ROI, save 450+ hours annually, and reduce costs by 10-50% through intelligent automation.

Complete guide to creating your Agrello account, starting your trial, and setting up your first workspace for digital document management.

A detailed guide to e-signature technology. Learn the difference between legal levels (AdES, QES) and technical formats (PAdES, XAdES, ASiC) as defined by eIDAS.

Learn how contract templates can dramatically accelerate your business processes. Discover the benefits of standardized agreements and how to create documents that empower your team to move faster.

Set up team collaboration in Agrello by inviting members, assigning roles, and organizing workspace access. Choose from Starter, Team, or Custom plans based on team size.
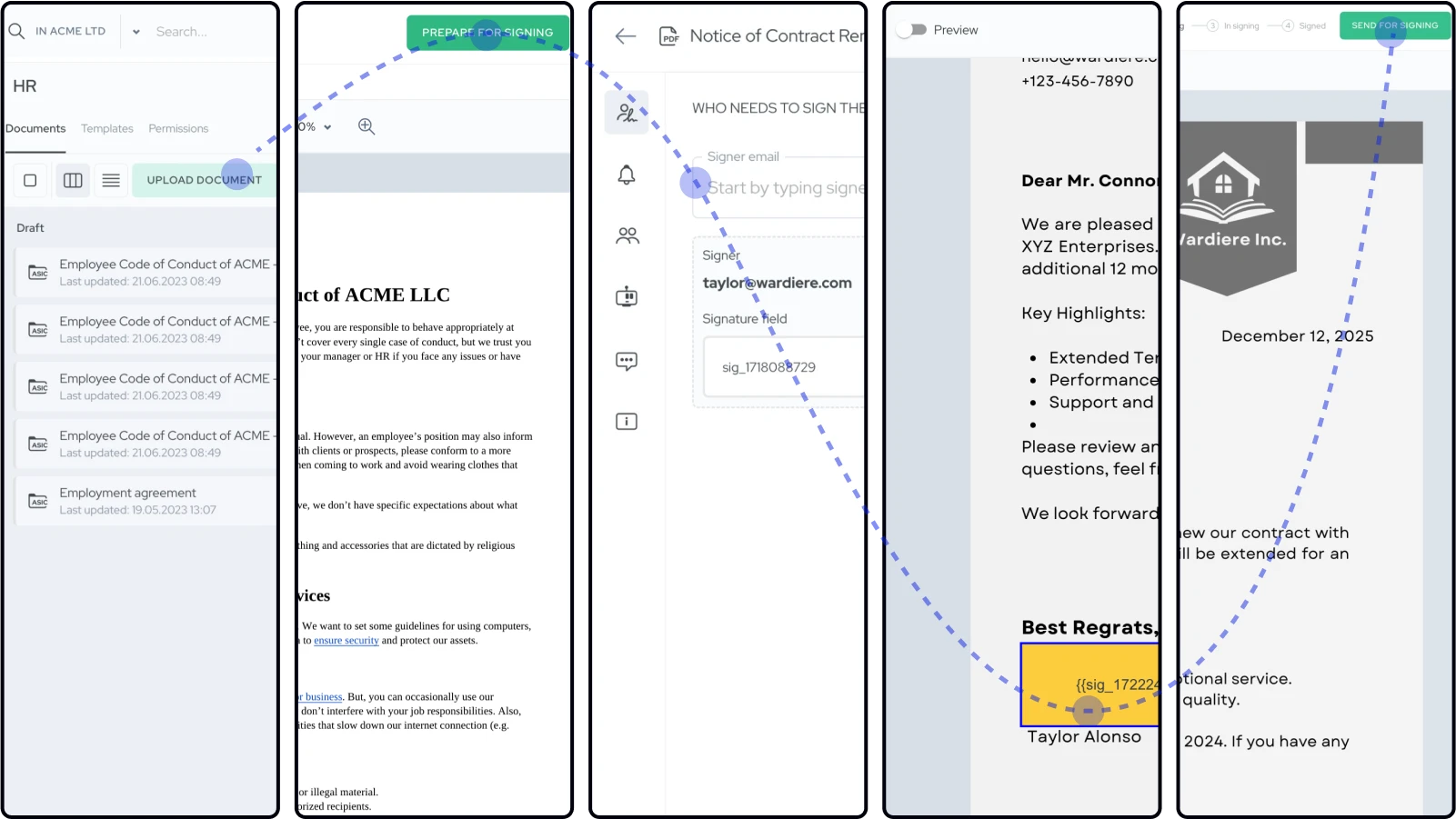
Master document lifecycle management from draft creation through signature collection. Learn to prepare documents, manage signers, send reminders, and track completion efficiently.

Enable self-service signing with shareable template links. Allow customers, partners, or employees to generate and sign documents on-demand without manual intervention.

Enable efficient document review with Agrello's commenting feature. Gather feedback from legal, stakeholders, and clients before sending for signature—even Viewers can comment.

Create and manage multi-file document packages using ASIC containers. Learn how to bundle contracts with attachments, technical specifications, and supporting documents into a single signed package.

Complete step-by-step implementation guide for AI-powered document automation. Learn proven methodologies, avoid common pitfalls, and achieve 248% ROI through strategic deployment.

Send your first document for signature in Agrello. Add signers, choose your format, place signature fields, and send - step by step.

A deep dive into PAdES signatures: what is their technical foundation, what is their legal standing, and why they are the standard for secure, long-term PDF signing.

Feeling overwhelmed by scattered contracts? Learn a simple, effective system for organizing your agreements, tracking key dates, and gaining the visibility you need to make smarter business decisions.

Export fillable field responses from templates to CSV format for seamless integration with CRM, HRIS, and analytics platforms. Eliminate manual data entry and automate downstream workflows.

Step-by-step guide for signing documents in Agrello. Learn how to access invitations, review documents, choose signature methods, and complete signing—no account needed.

Scale your contract operations with proven team collaboration workflows. Learn folder organization strategies, template standardization, department workflows, and cross-team coordination best practices.

Collect structured data from signers using fillable fields in templates. Learn {{curly_brackets}} syntax, PDF form fields, CSV export, and integration workflows for CRM and HRIS systems.

Discover how different industries leverage AI-powered document automation to transform operations. From healthcare's 30% administrative cost reduction to finance's 500% processing speed improvements.

Master document organization in Agrello with folders, subfolders, and advanced management features. Build efficient workflows that scale with your business.

Understand how ASiC containers and XAdES e-signatures team up to provide exceptionally secure, compliant, and long-lasting digital signatures across the EU.

Tired of contract approvals getting stuck? Learn how to fix the human side of contract management, eliminate bottlenecks, and create a smooth collaboration process that actually works.

Resolve common signing process issues including email delivery problems, signature method failures, non-responsive signers, and document corrections after sending.

Master document automation integration with comprehensive strategies for APIs, no-code platforms, and enterprise systems. Learn how organizations achieve 80-90% faster deployment through strategic integration approaches.

Master Agrello's template system to automate document creation. Learn dynamic field creation, bulk generation, and workflow optimization strategies.

Discover the most common contract management challenges facing SMBs and proven solutions to overcome them. Learn how to eliminate bottlenecks, reduce risks, and transform your contract processes.
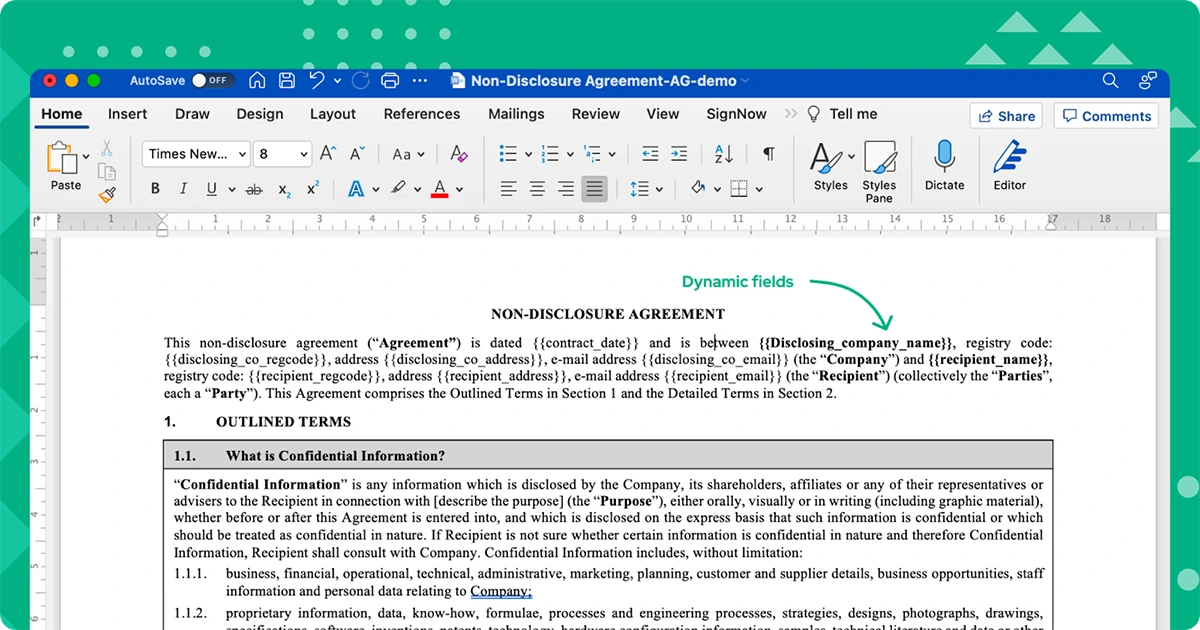
Master bulk document creation in Agrello to generate hundreds of personalized documents simultaneously. Perfect for employee agreements, customer contracts, and mass communications.

Comprehensive guide to e-signature security levels and authentication providers in Agrello. Learn about SES, AES, QES levels and choose the right signing method for your needs.