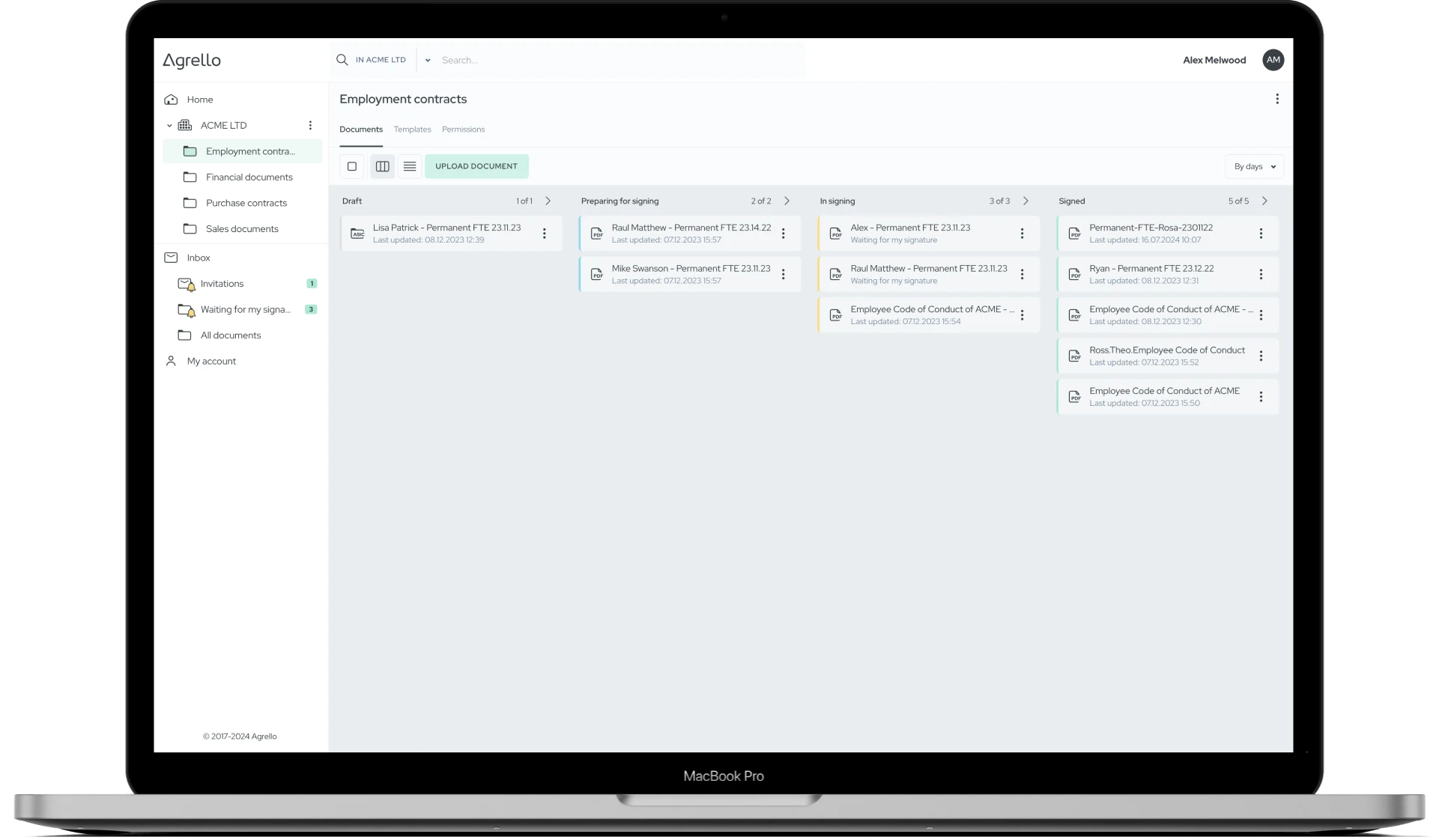
THE PROBLEM
Still struggling with manual contract workflows?
Printing, scanning, emailing, chasing signatures... Sound familiar?
Manual contract processes drain your time, create bottlenecks, and lead to missed deadlines. Your team deserves better than endless back-and-forth and version chaos.
PLATFORM FEATURES
Make your e-signing and contract management easier
Agrello streamlines every step — draft, sign, store, and track — so you can focus on real work.

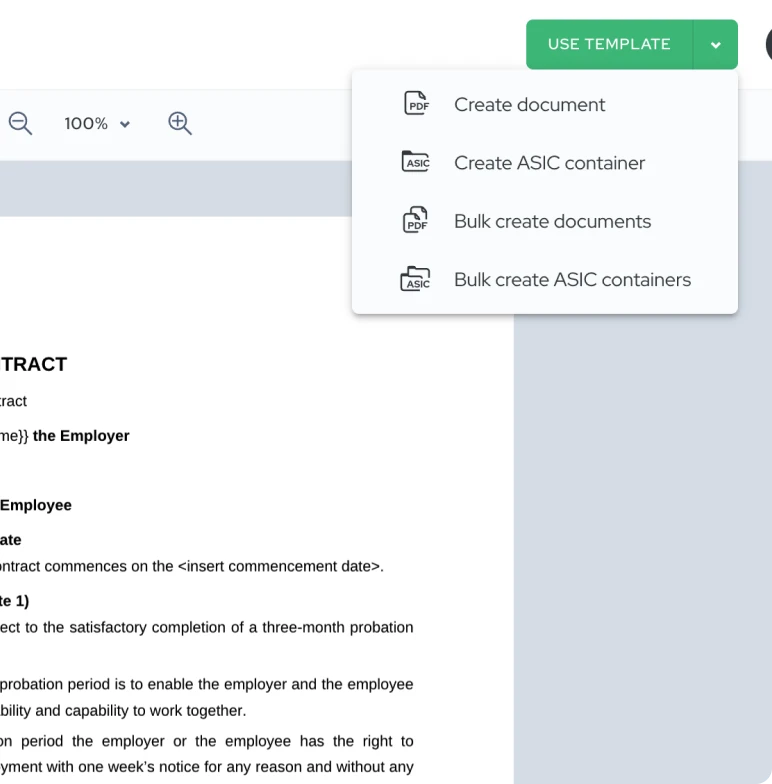
Create multiple contracts at once using Excel and Word templates
FEATURES
Say goodbye to manual data entry and errors
With Agrello, you can create contracts using Microsoft Word templates, just like you're used to. Need to generate multiple contracts at once?
Simply pull your data from an Excel spreadsheet, and let Agrello do the rest. In just a few clicks, you'll have professionally formatted contracts ready to send for e-signing.
What you can do with Agrello
From everyday signing to advanced automation — here is everything the platform offers.
Core
- ■Upload documents for signing (PDF, ASiC, eDOC, aDOC)
- ■Signing order
- ■Templates
- ■Commenting
- ■Reminders
- ■Audit trail
- ■Zapier support (5000+ integrations)
- ■Invitation email branding and custom messages
- ■User management
Signature methods
- ■Agrello e-Sign
- ■Baltic IDs (EE ID card, Smart-ID, LV eParaksts, EE & LT Mobile ID)
- ■Ukrainian Diia
- ■Swedish BankID
Automation and scale
- ■Bulk export files
- ■Bulk create
- ■Bulk sign
- ■Bulk actions (send, move, etc.)
- ■Editing documents on Agrello (DOCX, XLSX)
- ■Document numeration
Premium capabilities
- ■Agrello Forms & Applications
- ■Signing links (web)
- ■API access
- ■AI assistant
- ■Document approvals

OUR CUSTOMERS
Your business, simplified
Agrello's intuitive platform helps businesses of all sizes to simplify document workflows and enhance efficiency. Join a growing community of organizations streamlining their operations with ease.


Smarten saved a week's worth of manual work
Smarten Logistics uses the Agrello platform's reusable templates feature to create and sign new employment contracts on an ongoing basis.

FAST TRACK ONBOARDING
Book your free e-signing workshop!
In our workshop you can find out how to implement Agrello in your company without sacrificing your entire IT budget.
- Free practical workshop to explore e-signing and contract automation solutions.
- Step-by-step guidance on setting up the platform.
- Tips on how to seamlessly integrate Agrello into existing processes.
- Opportunity to ask questions and get advice from experts.
